情緒感知提示工程(Emotion-aware Prompt Engineering, EPE)是一種讓AI模型在回應時主動感知並理解用戶情緒的技術。核心做法是:
利用自然語言提示(Prompt)明確標記和描述使用者情緒
根據偵測到的情緒,自動調整語氣、回應內容與建議
這使得AI不只是理解語意,更能貼近用戶心理狀態,形成更同理、更人性化的互動。
情緒感知提示工程可以結合多種心理學理論,強化AI的溝通策略:
社會交換理論(Social Exchange Theory):強調互惠,AI可設計促進雙向交流與信任的語句。
"很高興能協助你,有什麼想法也歡迎分享"
權威效應(Obedience to Authority Study):明確設定AI的角色(如專家、諮商師),有利於用戶採納建議。但提示語氣需溫和,避免造成壓力。
"作為心理健康顧問,我建議你可以嘗試……,但最終決定權在你手中。"
共情(Empathy):EPE最常見理論。設計Prompt時加入同理語句、情緒鏡像、認可用戶感受,如「我明白你感到焦慮,這是很自然的反應」。
"我能理解你現在感到焦慮,這是很正常的情緒。讓我們一起面對這個挑戰。"
自我決定論(SDT):鼓勵自主選擇與行動,讓用戶覺得自己有控制權。
"你可以選擇自己感覺最舒適的方案,我能協助分析利弊"
範例:
客服機器人根據使用者回答,決定下一步追問或建議




範例(見上圖二CoT段):
感知表達情緒 → 2. 理解並認可 → 3. 給予支持 → 4. 有需要才給建議
範例:
遇到複雜選擇題,AI分枝評估各種可能路徑,再選出最佳方案
範例:
用戶問:「今年諾貝爾獎誰得的?」AI發現知識庫沒資料,就自動搜尋最新資訊再回答
實作放在colab
實作示意圖:
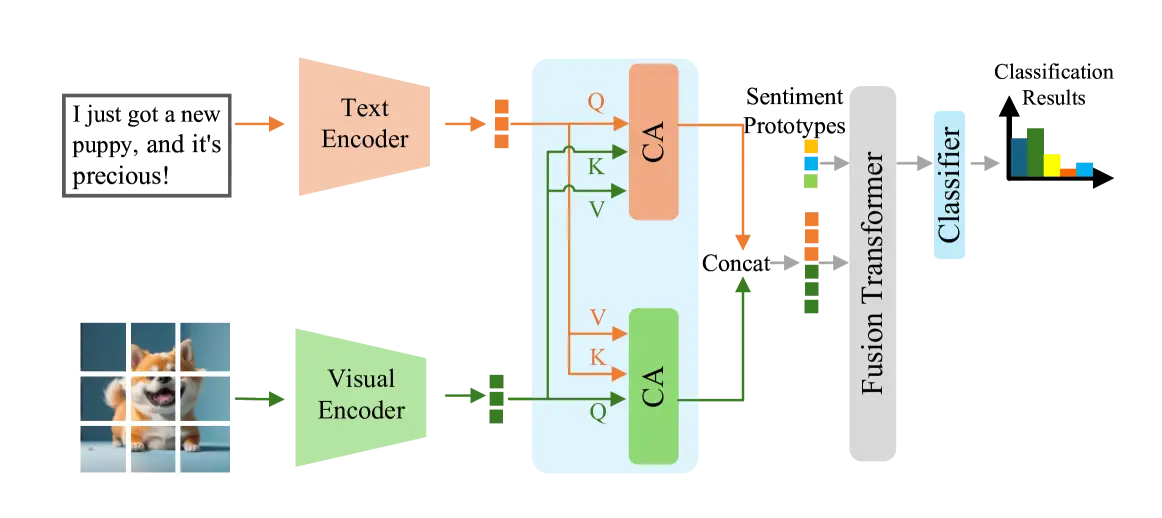
所謂Fusion Transformer的監督式對比學習,將不同情緒原型有效分辨
如下圖: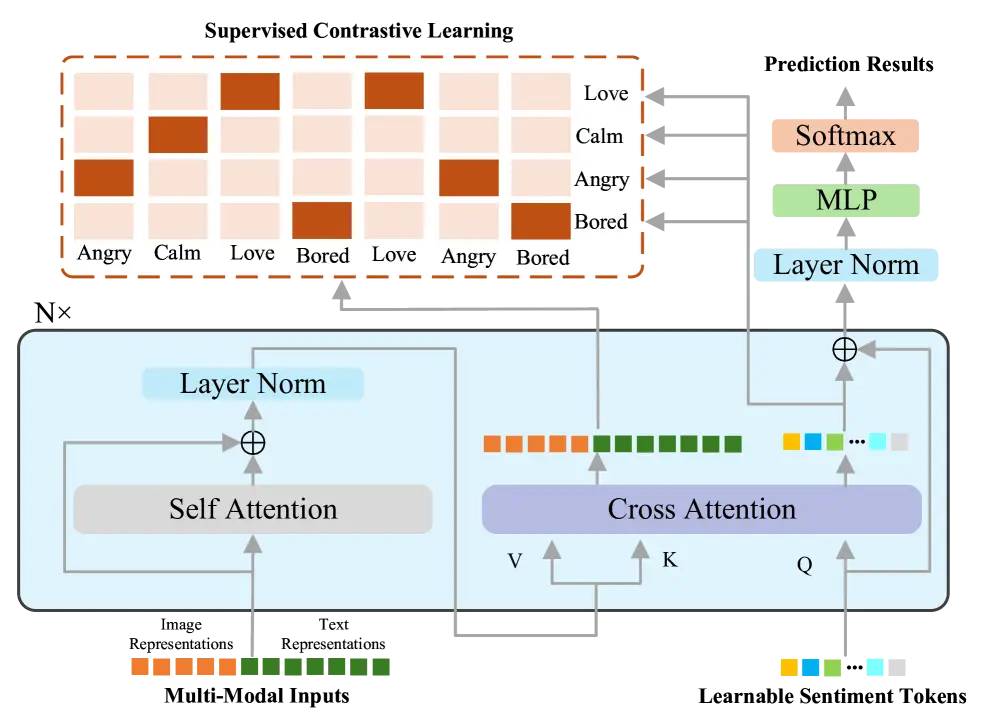
參考自:https://arxiv.org/html/2509.03212v1
由上圖可見,AIVA的多模態情緒感知關鍵在於利用Transformer架構自動融合各種情緒訊號(如圖像、文本),再結合監督式對比學習,將不同情緒原型有效分辨。
由COT的圖可見,設計Prompt時可結合:
明確角色設定(Role)
貼近情緒的Few-Shot例句
歷史情緒交互記錄(History)
Chain of Thought分步推理(CoT)
用戶輸入 → 情緒識別 → 心理需求分析 → 理論選擇 → 提示生成 → AI回應 → 效果評估
實作放在colab
def __init__(self, gemini_api_key, use_pretrained_text_model=False, text_model_path=None):
"""
初始化情緒感知AI系統
Args:
gemini_api_key (str): Gemini API金鑰
use_pretrained_text_model (bool): 是否使用預訓練的文字情緒模型
text_model_path (str): 文字情緒分析模型路徑(可選)
"""
# 設置Gemini API
genai.configure(api_key=gemini_api_key)
self.gemini_model = genai.GenerativeModel('gemini-2.5-flash')
# 情緒標籤
self.text_emotion_labels = ['angry', 'fear', 'happy', 'love', 'sadness', 'surprise']
# 初始化文字情緒分析
self.use_pretrained_text_model = use_pretrained_text_model
self.text_emotion_model = None
self.vectorizer = None
2.1 情緒分析器
實現了一個多模式的情緒分析類別,包含基於規則的文字情緒分析、基於預訓練模型的文字情緒分析,以及利用DeepFace進行圖像情緒分析的功能。
def _init_rule_based_emotion_analyzer(self):
"""
初始化規則基礎的情緒分析器
"""
# 情緒關鍵字字典
self.emotion_keywords = {
'angry': ['生氣', '憤怒', '氣死', '火大', '怒', '討厭', '煩躁', '惱火', '不爽'],
'fear': ['害怕', '恐懼', '擔心', '焦慮', '緊張', '不安', '恐慌', '驚慌', '畏懼'],
'happy': ['開心', '快樂', '高興', '愉快', '興奮', '喜悅', '滿足', '幸福', '棒', '好'],
'love': ['愛', '喜歡', '珍惜', '感謝', '溫暖', '甜蜜', '浪漫', '心動', '感動'],
'sadness': ['難過', '傷心', '沮喪', '憂鬱', '失落', '痛苦', '絕望', '哭', '眼淚', '挫折'],
'surprise': ['驚訝', '意外', '震驚', '不敢相信', '沒想到', '居然', '竟然', '哇']
}
def analyze_text_emotion_rule_based(self, text):
"""
基於規則的文字情緒分析
Args:
text (str): 輸入文字
Returns:
tuple: (預測情緒, 信心度)
"""
text = text.lower()
emotion_scores = {emotion: 0 for emotion in self.text_emotion_labels}
# 計算每種情緒的分數
for emotion, keywords in self.emotion_keywords.items():
for keyword in keywords:
if keyword in text:
emotion_scores[emotion] += 1
# 找出最高分的情緒
if max(emotion_scores.values()) == 0:
return 'happy', 0.3 # 預設為中性偏正面
dominant_emotion = max(emotion_scores, key=emotion_scores.get)
max_score = emotion_scores[dominant_emotion]
total_words = len(text.split())
confidence = min(max_score / max(total_words, 1), 1.0)
return dominant_emotion, confidence
def analyze_text_emotion(self, text):
"""
分析文字情緒
Args:
text (str): 輸入文字
Returns:
tuple: (預測情緒, 信心度)
"""
# 使用預訓練模型
if self.vectorizer:
# 如果有向量化器,先進行向量化
text_vectorized = self.vectorizer.transform([text])
predictions = self.text_emotion_model.predict_proba(text_vectorized)
# 獲取預測結果
if hasattr(predictions, 'shape') and len(predictions.shape) > 1:
emotion_idx = np.argmax(predictions[0])
confidence = np.max(predictions[0])
# 確保索引在範圍內
if emotion_idx < len(self.text_emotion_labels):
return self.text_emotion_labels[emotion_idx], confidence
def analyze_image_emotion(self, image_path):
"""
使用DeepFace分析圖像情緒
Args:
image_path (str): 圖像路徑
Returns:
dict: 情緒分析結果
"""
# 使用DeepFace進行情緒分析
result = DeepFace.analyze(
img_path=image_path,
actions=['emotion'],
enforce_detection=False,
silent=True
)
# 獲取主要情緒
if isinstance(result, list):
emotions = result[0]['emotion']
dominant_emotion = max(emotions, key=emotions.get)
confidence = emotions[dominant_emotion] / 100.0 # 轉換為0-1範圍
return {
'dominant_emotion': dominant_emotion,
'confidence': confidence,
'all_emotions': emotions
}
def _get_default_image_emotion(self):
"""
返回預設的圖像情緒分析結果
"""
return {
'dominant_emotion': 'neutral',
'confidence': 0.5,
'all_emotions': {'neutral': 50.0}
}
2.2 文字預處理(用於預訓練模型)
具體步驟包括:
將輸入文字轉成小寫並切分成單詞列表。
將每個單詞使用簡單的雜湊函數轉換為一個介於0到9999之間的整數,以數字序列形式表示(One-Hot Encoding)。
限制序列長度最多100個詞,超過部分截斷,不足部分用0填充到固定長度100。
最後輸出形狀為(1, 100)的numpy陣列,方便作為模型輸入的特徵格式。
def _preprocess_text(self, text):
"""
文字預處理(用於預訓練模型)
Args:
text (str): 原始文字
Returns:
np.array: 預處理後的文字特徵
"""
# 簡單的文字預處理
# 實際使用時需要根據你的模型調整
max_length = 100
# 將文字轉換為數字序列(這是簡化版本)
words = text.lower().split()
sequence = [hash(word) % 10000 for word in words[:max_length]]
# 填充到固定長度
if len(sequence) < max_length:
sequence.extend([0] * (max_length - len(sequence)))
return np.array([sequence])
2.3 根據用戶的文字輸入或圖像,用gemini生成具有同理心的回應
def generate_empathetic_response(self, user_input, image_path=None):
"""
生成具有同理心的回應
Args:
user_input (str): 用戶輸入文字
image_path (str, optional): 用戶上傳的圖像路徑
Returns:
dict: 包含分析結果和AI回應的字典
"""
# 分析文字情緒
text_emotion, text_confidence = self.analyze_text_emotion(user_input)
# 分析圖像情緒(如果有提供)
image_emotion_result = None
if image_path and os.path.exists(image_path):
image_emotion_result = self.analyze_image_emotion(image_path)
image_emotion = image_emotion_result['dominant_emotion']
# 生成共情提示
prompt = self._create_empathy_prompt(user_input, text_emotion, text_confidence, image_emotion)
# 使用Gemini生成回應
response = self.gemini_model.generate_content(prompt)
ai_response = response.text
return {
'text_emotion': {
'emotion': text_emotion,
'confidence': text_confidence
},
'image_emotion': image_emotion_result,
'ai_response': ai_response,
'prompt_used': prompt
}
3.1 生成Prompt範本
def _create_empathy_prompt(self, user_input, text_emotion, text_confidence, image_emotion):
"""
創建共情提示
"""
return f"""
你是一位具有同理心與情緒感知能力的AI助手。
用戶狀況:{user_input}
文字情緒:{text_emotion} (信心度: {text_confidence:.2f})
圖像情緒:{image_emotion}
請根據以上多模態情緒資訊,提供溫暖、理解且有建設性的回應:
1. 首先認可用戶的情緒感受
2. 提供同理心支持
3. 給出具體可行的建議
4. 鼓勵用戶表達更多想法
回應風格要溫和、專業且充滿人文關懷。請用繁體中文回應。
"""
def _generate_fallback_response(self, user_input, emotion):
"""
生成預設回應(當API失效時)
"""
emotion_responses = {
'angry': "我能感受到你的憤怒和挫折感。這些情緒是完全可以理解的。讓我們一起想想如何處理這個問題。",
'fear': "我理解你現在可能感到不安或擔心。面對未知確實會讓人緊張,但我們可以一步步來解決。",
'happy': "很高興看到你的積極態度!讓我們繼續保持這份正面能量。",
'love': "感謝你分享這份溫暖的感受。正面的情感總是能帶來力量。",
'sadness': "我能感受到你現在的難過。雖然現在很艱難,但請記住這些情感都是暫時的,我們會一起度過。",
'surprise': "看起來你遇到了意想不到的情況!讓我們一起分析一下這個狀況。"
}
base_response = emotion_responses.get(emotion, "我理解你現在的感受。讓我們一起來看看如何幫助你。")
return f"{base_response}\n\n關於你提到的:「{user_input}」,我建議我們可以從以下幾個角度來思考解決方案。你願意告訴我更多細節嗎?"
3.2 測試情緒感知AI系統
# 測試和使用範例
def test_emotion_ai():
"""
測試情緒感知AI系統
"""
# 設置API金鑰(請替換為你的實際金鑰)
GEMINI_API_KEY = "YOUR_GEMINI_API_KEY"
# 初始化系統(不使用預訓練模型)
emotion_ai = EmotionAwareAI(
gemini_api_key=GEMINI_API_KEY,
use_pretrained_text_model=False
)
# 測試範例
test_cases = [
"我搞不定這個功能,感覺很挫折",
"今天工作很順利,心情超好的!",
"有點擔心明天的面試,好緊張",
"謝謝你的幫忙,真的很感謝"
]
print("=== 情緒感知AI測試 ===\n")
for i, user_input in enumerate(test_cases, 1):
print(f"測試 {i}: {user_input}")
print("-" * 50)
# 生成回應
result = emotion_ai.generate_empathetic_response(user_input)
# 輸出結果
text_emotion = result['text_emotion']
print(f"檢測到的情緒: {text_emotion['emotion']} (信心度: {text_emotion['confidence']:.2f})")
print(f"AI回應: {result['ai_response']}")
print("\n" + "="*80 + "\n")
3.3 修復模型載入的輔助函數
常見的模型格式則有:
.pkl(pickle):通常用於保存傳統機器學習模型,是Python專用序列化格式。
.h5 / .keras:Keras深度學習模型格式,完整保存模型架構和權重。
ONNX(Open Neural Network Exchange):跨平台的深度學習模型格式,方便模型在不同框架間轉換。
TensorFlow SavedModel:TensorFlow標準格式,保存模型結構與權重。
# 修復模型載入的輔助函數
def check_model_file(model_path):
"""
檢查模型文件是否完整
Args:
model_path (str): 模型文件路徑
Returns:
dict: 檢查結果
"""
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
return {"status": "not_found", "message": "模型文件不存在"}
# 檢查文件大小
file_size = os.path.getsize(model_path)
print(f"模型文件大小: {file_size / (1024*1024):.2f} MB")
# 根據文件副檔名選擇載入方式
if model_path.endswith('.pkl'):
# 嘗試載入pickle文件
with open(model_path, 'rb') as f:
model_data = pickle.load(f)
return {"status": "success", "message": "Pickle模型載入成功", "model": model_data}
elif model_path.endswith(('.h5', '.keras')):
# 嘗試載入Keras模型
model = tf.keras.models.load_model(model_path)
return {"status": "success", "message": "Keras模型載入成功", "model": model}
else:
return {"status": "error", "message": "不支援的文件格式"}
情緒感知提示工程(EPE)整合多模態感知技術、心理學理論與進階提示工具,讓AI互動不僅有語義理解,更能貼合人性情感,適用於情感陪伴、智能客服、健康諮詢等多種場景。
